Anatomy of the Neck for Otolaryngology Examinations

European Board of Otorhinolaryngology Examinations: A Gateway to Professional Excellence in ENT
The European Board of Otorhinolaryngology Examinations (EBEORL-HNS) represents a hallmark of quality and expertise in the field of ear, nose, and throat (ENT) care. Established by the UEMS ORL Section and Board in October 2008, EBEORL-HNS aims to harmonize the knowledge base among otolaryngologists in Europe, enhancing the free movement of specialists between member countries.
Overview of EBEORL-HNS
EBEORL-HNS operates as an independent entity, working in collaboration with various otolaryngology associations to develop and administer comprehensive examinations. These exams are designed to evaluate the skills, expertise, and competence of otolaryngologists, ensuring a high standard of care across Europe.
Certification Process
The certification process involves two parts: a written exam with 100 multiple-choice questions, and an oral exam. The written part must be passed to qualify for the oral exam. Successful candidates are awarded the title “Fellows of the European Board of ORL-HNS” or receive a “Diploma of the European Board of Otorhinolaryngology.”
Application and Exam Details for 2024
- Registration: Open for the Part I online exam in 2024.
- Exam Date: Part I is scheduled for Saturday, 20th April 2024.
- Application Deadline: The deadline is 20th March 2024.
- Exam Fee: 600€.
- Eligibility: Candidates should be qualified specialists in ORL-HNS or in their final year of training.
- Application Process: Candidates need to fill out an application form and provide all required official documents, translated into English.
Standardization and Training
Through its rigorous certification process, EBEORL-HNS ensures a standardized and high-quality level of training across Europe, contributing significantly to patient safety and care.
Collaboration and Professional Development
EBEORL-HNS maintains a close relationship with national otolaryngology societies, ensuring that its examinations reflect the latest advancements in the field. It also fosters continuous professional development among ENT specialists.
International Recognition
EBEORL-HNS certification is internationally recognized, facilitating professional mobility and exchange of expertise globally. It is an additional qualification to national education/exams, offering a range of benefits including proof of standard in UEMS affiliated countries, academic and job promotion, and higher salary prospects in some cases.
Conclusion
EBEORL-HNS plays a pivotal role in elevating otolaryngology standards in Europe. Its certification process, commitment to training standardization, continuous professional development emphasis, and international recognition mark it as a beacon of excellence in ENT care.
References
Endolymphatic Sac Surgery for Otolaryngology Examinations
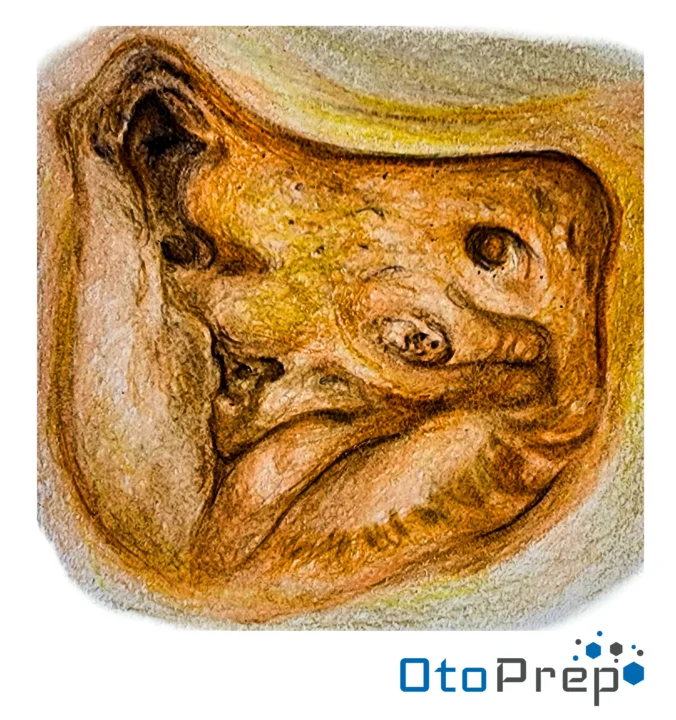
Anatomy and Physiology
The endolymphatic sac is an extension of the membranous labyrinth, located in the posterior part of the temporal bone. It regulates endolymphatic fluid pressure and volume, crucial for inner ear function.
How well do you know Endolymphatic Sac Anatomy?
Identify these structures on the image above:1. Horizontal semicircular canal
2. Facial nerve
3. Posterior semicircular canal
4. Endolymphatic sac
5. Posterior fossa dura
6. Sigmoid sinus
- Horizontal semicircular canal: Detects angular acceleration.
- Facial nerve: Responsible for facial expression and taste sensation.
- Posterior semicircular canal: Also involved in detecting angular acceleration.
- Endolymphatic sac: Regulates endolymphatic fluid pressure and volume.
- Posterior fossa dura: Outermost layer of the meninges in the posterior fossa.
- Sigmoid sinus: Drains blood from the brain towards the heart.
Pathology and Pathophysiology
Endolymphatic sac surgery is primarily indicated in the treatment of Meniere's disease, believed to be related to an imbalance in endolymph production and absorption.
- Meniere's Disease: Characterized by vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, and aural fullness.
- Endolymphatic Hydrops: Excessive accumulation of endolymph in the inner ear.
Endolymphatic sac surgery aims to reduce endolymphatic pressure through decompression or diversion of fluid. It may involve exposing the sac by removing bone and dura, followed by shunt placement or sac decompression.
Otolaryngology Examination Questions
- Indications for Surgery: "What conditions indicate endolymphatic sac surgery, and what are the expected outcomes?"
- Surgical Approach: "Describe the surgical approach to the endolymphatic sac for decompression in Meniere's disease."
- Complications: "What are the potential complications of endolymphatic sac surgery?"
- Anatomical Considerations: "Discuss the anatomical structures at risk during endolymphatic sac surgery."
Anatomy of the Neck for Otolaryngology Examinations

Anatomy, Physiology, Pathology, and Pathophysiology of the Neck
The neck is a vital area in otolaryngology, encompassing critical structures. Its comprehensive understanding is essential for otolaryngologists, particularly for examinations and surgical procedures.
How well do you know the Neck?
Identify these structures on the image above:1. Hypoglossal nerve
2. Posterior belly of digastric
3.Facial artery
4. External carotid artery
5. Internal carotid artery
6. Spinal accessory nerve
7. Sternocleidomastoid Muscle
8. Vagus nerve 9. Omohyoid
10. Superior thyroid artery
11. Superior laryngeal artery
12. Lingual artery
Anatomy and Physiology of the Neck
The neck is intricately layered, demarcated into compartments, and contains vital anatomical structures. It is pivotal in various physiological processes and surgical interventions.
- Hypoglossal nerve: Essential for tongue movement.
- Posterior belly of digastric: Assists in mandibular movement.
- Facial artery: Crucial for facial blood supply.
- External carotid artery: Supplies blood to the face and neck.
- Internal carotid artery: Provides blood to the brain.
- Spinal accessory nerve: Innervates neck muscles.
- Sternocleidomastoid: Involved in head rotation and flexion.
- Vagus nerve: Plays a role in parasympathetic control.
- Internal jugular vein: Drains blood from the brain, face, and neck.
- Omohyoid: Depresses the hyoid bone.
- Superior thyroid artery: Supplies blood to the thyroid gland.
- Superior laryngeal artery: Blood supply to the larynx.
- Lingual artery: Supplies blood to the tongue and mouth floor.
Pathology and Pathophysiology
Neck pathologies encompass a range of conditions that can significantly impact patient health. These conditions require accurate diagnosis and effective management.
- Neck Trauma: Can lead to critical injuries affecting nerves, arteries, and muscles in the neck.
- Metastatic Neck Disease: Often seen in head and neck cancers, requiring comprehensive neck dissection.
- Chronic Otitis Media: May involve the epitympanum, with implications for middle ear function.
- Vascular Anomalies: Variations in neck vasculature can present unique challenges during surgical procedures.
- Neurological Disorders: Conditions affecting cranial nerves can have profound impacts on speech, swallowing, and head movement.
Potential Examination Questions
- Role and injury implications of the hypoglossal nerve in neck dissection.
- Identification and roles of arteries in neck surgeries.
- Function and surgical considerations for the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
- Diagnostic approaches and treatment modalities for neck trauma.
- Implications of vascular anomalies on neck surgeries.
- Clinical presentations and management of neurological disorders in the neck.
- Identification and management of metastatic diseases in the neck.
- Role of imaging in diagnosing pathologies of the neck.
Exploring the Epitympanum: Anatomy, Pathology, and Examination Questions

Epitympanum Anatomy in Otolaryngology Examinations
Introduction to the Epitympanum
The epitympanum, also known as the attic or epitympanic recess, is the most superior portion of the tympanic cavity. It is a compact and small air-filled space, positioned above the eardrum and beneath the tegmen tympani, playing a crucial role in sound transmission and in various ear conditions.
How well do you know the Epitympanum?
Identify these structures on the image above:1. Chorda tympani
2. Cog
3.Facial nerve
4. Tensor tympani
5. Processus Cochleariformis
6. Stapedial tendon
7. Lenticular process
8. Posterior crus 9. Stapes footplate
10. Anterior crus
11. Manubrium
12. Umbo
Anatomical Structures in the Epitympanum
- Chorda Tympani: Nerve carrying taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue and supplying parasympathetic fibers to the submandibular and sublingual glands.
- Cog: Bony ridge separating compartments in the epitympanum.
- Facial Nerve: Travels through the facial canal in the temporal bone, just medial to the epitympanum.
- Tensor Tympani: Muscle dampening the vibrations of the tympanic membrane.
- Processus Cochleariformis: Bony eminence serving as the fulcrum for the tensor tympani muscle.
- Stapedial Tendon: Connects the stapedius muscle to the stapes bone.
- Lenticular Process: Small projection from the incus articulating with the stapes.
- Posterior Crus: One of the two limbs of the stapes bone.
- Stapes Footplate: Fits into the oval window between the middle ear and the inner ear.
- Anterior Crus: Other limb of the stapes bone.
- Manubrium: Handle-like part of the malleus attached to the tympanic membrane.
- Umbo: Most depressed point of the tympanic membrane, at the end of the manubrium of the malleus.
Pathologies in the Epitympanum
Conditions like cholesteatoma and chronic otitis media can affect the epitympanum, leading to disorders such as tympanic membrane abnormalities and middle ear tumors.
Potential Examination Questions
- Anatomy: "Identify the structures found in the epitympanum separated by the Cog."
- Pathology: "Discuss the implications of cholesteatoma in the epitympanum."
- Diagnostic Procedures: "What are the diagnostic imaging modalities for assessing the epitympanum?"
- Treatment: "What surgical approaches are used for treating pathologies in the epitympanum?"
- Clinical Scenarios: "A patient presents with hearing loss and discharge; suspecting an epitympanic involvement, what are your diagnostic steps?"
Understanding the Internal Acoustic Meatus for Otolaryngology Examinations
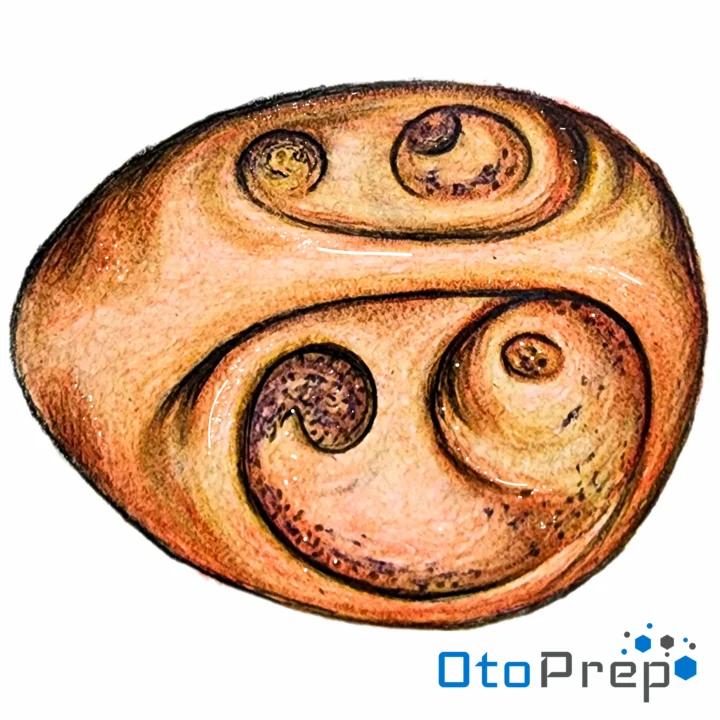
Anatomy of the Internal Auditory Meatus
The Internal Auditory Meatus (IAM), also known as the Internal Acoustic Canal, is a bony canal within the petrous portion of the temporal bone. It plays a pivotal role in transmitting nerves and vessels from within the posterior cranial fossa to the auditory and vestibular apparatus.
Below is a detailed exploration of the key structures visible within the IAM:
- Bill’s Bar: Also known as the vertical crest or crista verticalis, this landmark divides the superior compartment of the IAM into anterior and posterior compartments. It houses the facial nerve (CN VII) and superior division of the vestibular nerve.
- Fallopian Canal: This bony canal allows the facial nerve to traverse the petrous temporal bone, housing the facial nerve (CN VII) responsible for facial expression, taste sensation, and more.
- Superior Vestibular Nerve: A component of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII), responsible for transmitting balance and spatial orientation information from the utricle and semicircular canals.
- Transverse Crest: Also known as the falciform crest, this horizontal ridge separates the IAM into superior and inferior parts.
- Inferior Vestibular Nerve: Another component of CN VIII, it transmits balance information from the saccule and posterior semicircular canal.
- Cochlear Nerve: Responsible for transmitting auditory information from the cochlea to the brain, situated anteriorly in the inferior IAM.
- Foramen Singulare: A thin channel that carries the singular nerve from the internal auditory canal, medially located to the inferior vestibular area.
Understanding the anatomy and relationship of these structures is crucial in the management of diseases involving the IAM.
How well do you know the IAM?
Identify these structures on the image above:1. Bill's Bar
2. Fallopian Canal
3.Superior Vestibular Nerve
4. Transverse Crest
5. Inferior Vestibular Nerve
6. Cochlear Nerve
7. Foramen Singulare
Understanding the Internal Acoustic Meatus for Otolaryngology Examinations
The internal acoustic meatus (IAM), or Internal Acoustic Canal, is a vital anatomical structure in otolaryngology. It plays a significant role in transmitting nerves and vessels associated with auditory and vestibular functions. In board examinations, questions related to the IAM may cover a wide range of topics, including its anatomy, associated pathologies, and clinical scenarios.
Potential Examination Questions:
- Anatomy and Physiology: Questions might explore the anatomical structures passing through the IAM and their roles in auditory and vestibular functions.
- Pathology: Focus on diseases affecting the IAM, such as vestibular schwannomas, and their clinical manifestations.
- Diagnostic Procedures: Questions may inquire about the diagnostics, like MRI, used to evaluate IAM pathologies.
- Treatment: Queries about management options for conditions like vestibular schwannomas.
- Clinical Scenarios: Presentations of clinical scenarios involving the IAM and related decision-making processes.
These questions test a candidate's knowledge in recalling information, interpreting clinical data, and problem-solving in otolaryngology-head and neck surgery.
Deciphering the Medial Wall of the Middle Ear

Deciphering the Medial Wall of the Middle Ear: An Interactive Anatomy Guide
The human auditory system is a fascinating and complex structure, and its central chamber, the middle ear, is a focus for otolaryngology examinations and clinical diagnosis. This article provides an in-depth look at the medial wall of the middle ear, also known as the labyrinthine wall, which features prominently in Otolaryngology Examinations.How well do you know the medial wall of the middle ear?
Identify these structures on the image above:1. Prussak's Space
2. Lateral Process of Malleus
3. Manubrium of Malleus
4. Umbo of Malleus
5. Long Process of Incus
6. Lenticular Process of Incus
7. Stapedial Ligament
8. Posterior Sinus
9. Pyramidal Eminence
10. Stapes Footplate
11. Ponticulus
12. Sinus Tympani
13. Subiculum
14. Promontory
15. Round Window Niche
16. Finiculus
17. Eustachian Tube
18. Processus Cochleariformis
19. Tensor Tympani
20. Jacobson's Nerve.
The Vital Structures
- Prussak's Space: A crucial area prone to cholesteatoma formation, bordered by Shrapnell's membrane and the scutum.
- Lateral Process of Malleus: Visible during otoscopic examination, this is a key landmark in the tympanic membrane.
- Manubrium of Malleus: This handle-like structure transmits sound vibrations to the incus.
- Umbo of Malleus: The concave tip of the manubrium and a central examination point for eardrum retraction.
- Long Process of Incus: Essential for sound conduction, this process articulates with the stapes.
- Lenticular Process of Incus: Facilitates the vibration transfer from the incus to the stapes.
- Stapedial Ligament: Provides stability for the stapes, the smallest bone in the body.
- Posterior Sinus: A depression with surgical significance in the tympanic cavity.
- Pyramidal Eminence: Houses the stapedius muscle, critical for dampening sounds.
- Stapes Footplate: Fits into the oval window and is central to sound transmission to the inner ear.
- Ponticulus: A small bony bridge in the posterior wall of the tympanic cavity.
- Sinus Tympani: A deep recess behind the oval window in the medial wall of the tympanic cavity.
- Subiculum: A small area located at the entrance to the sinus tympani.
- Promontory: A rounded prominence on the medial wall of the tympanic cavity, formed by the first turn of the cochlea.
- Round Window Niche: A small hollow area in the medial wall of the tympanic cavity that houses the round window of the cochlea.
- Finiculus: A small, cord-like structure in the tympanic cavity.
- Eustachian Tube: A tube that connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx, allowing for the equalization of pressure on either side of the eardrum.
- Processus Cochleariformis: A small, hook-like bone in the tympanic cavity that serves as a pulley for the tendon of the tensor tympani muscle.
- Tensor Tympani: A small muscle in the middle ear that dampens the vibrations of the tympanic membrane by pulling on the manubrium of the malleus.
- Jacobson's Nerve: Also known as the tympanic nerve, this is a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve that provides sensory innervation to the middle ear.
These structures play crucial roles in the transmission of sound from the external environment to the inner ear, where it is converted into electrical signals and interpreted by the brain. Understanding their anatomy is essential for otolaryngologists, as it aids in the diagnosis and treatment of various ear conditions.
Understanding the Middle Meatus and Tympanic Cavity Segments
The middle meatus, a key component of nasal anatomy, and various segments of the tympanic cavity play integral roles in the function and health of the ear and nose. Detailed knowledge of these structures is essential in otolaryngology, particularly for understanding pathologies and surgical approaches.
Middle Meatus and Tympanic Cavity Segments
The middle meatus can be divided into several segments, including the hypotympanum, epitympanum, mesotympanum, protympanum, and retrotympanum. Each segment has distinct anatomical features and functions:
- Hypotympanum: Located inferior to the tympanic membrane, this crescent-shaped space at the bottom of the middle ear is crucial for the drainage and function of the middle ear.
- Epitympanum: Also known as the attic, the epitympanum is the most superior portion of the tympanic cavity, containing important auditory ossicles.
- Mesotympanum: The central part of the tympanic cavity, the mesotympanum houses most of the middle ear's crucial structures and is pivotal for sound transmission.
- Protympanum: Anterior to the tympanic cavity, the protympanum contains the bony portion of the Eustachian tube, playing a role in ear ventilation and pressure regulation.
- Retrotympanum: The retrotympanum features various sinuses and recesses, making up the complex posterior aspect of the tympanic cavity.
For otolaryngologists and students, an in-depth understanding of these segments aids in the accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of ear and nasal conditions.
Interactive Image With Solutions
References
Mastering Statistical Analysis for Otolaryngology Exams


Mastering Statistical Analysis for Otolaryngology Exams
Introduction
Understanding the fundamentals of statistical analysis is crucial for aspiring otolaryngologists preparing for board exams. This article explores key statistical concepts and their application in otolaryngology, focusing on the three main exams: FRCS (Fellowship of the Royal Colleges of Surgeons), EBEORL (European Board Examination in Otorhinolaryngology), and the American Boards.Quiz: Test Your Knowledge
Try 15 of our Questions on this specific topic for FREE!Podcast: Decoding Statistics in Otolaryngology
Listen to a 10 minute discussion on various uses of statistics in OtolaryngologyKey Statistical Concepts and Techniques
Statistical analysis forms the backbone of evidence-based practice in otolaryngology. Key concepts include:- Categorical Data: Understanding nominal, ordinal, and binary data through examples like throat infection types and sleep apnea severity.
- Numerical Data: Dissecting discrete and continuous data with cases such as sinusitis episodes and audiometry scores.
- Data Structure: From univariate to multivariate data, learn how each type is used in clinical research.
- Data Distribution: Grasping normal and non-normal distributions and their implications in otolaryngological studies.
- Statistical Methodology: Applying parametric and non-parametric statistics in various clinical scenarios.
- Time Dimension: Differentiating between cross-sectional, time series, longitudinal, and panel data.
- Special Characteristics: Tackling spatial, survival, ranked, complex survey, hierarchical, network, and text data.
| Statistical Test | Data Type | When to Use | Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paired t-test | Continuous, Normally distributed | Comparing means of two related groups or matched pairs | Comparing the same group’s measurements at two different times |
| Unpaired t-test | Continuous, Normally distributed | Comparing means of two independent groups | Comparing two different groups’ measurements |
| Mann-Whitney U test | Ordinal, Non-parametric | Comparing two independent groups when data are not normally distributed | Comparing two different groups’ measurements |
| Wilcoxon Signed Rank test | Ordinal, Non-parametric | Comparing two related samples or repeated measurements on a single sample | Comparing the same group’s measurements at two different times |
| Wilcoxon matched pairs test | Ordinal, Non-parametric | Comparing two related samples or repeated measurements on a single sample | Comparing the same group’s measurements at two different times |
| Kruskal Wallis test | Ordinal, Non-parametric | Comparing more than two independent groups when data are not normally distributed | Comparing multiple different groups’ measurements |
| One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) | Continuous, Normally distributed | Comparing means of more than two independent groups | Comparing multiple different groups’ measurements |
| Two-way Analysis of Variance | Continuous, Normally distributed | Comparing means across two independent variables and their interaction | Assessing the interaction effect between two different independent variables |
| Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient | Ordinal, Non-parametric | Assessing the association between two ranked variables | Determining the relationship between two ordinal variables |
| Pearson’s correlation coefficient | Continuous, Normally distributed | Measuring the linear relationship between two continuous variables | Assessing the linear relationship between two continuous variables |
| Fisher’s exact test | Categorical | Analyzing the association between two categorical variables, especially in small samples | Comparing categorical data in small sample sizes |
| X2 test | Categorical | Determining if there is a significant association between two categorical variables | Comparing categorical data in larger sample sizes |
| Friedman Test | Ordinal, Non-parametric | Comparing three or more paired groups | Comparing the same group’s measurements at three or more different times |
| Poisson analysis | Count data | Used for analyzing count data and rates, typically for rare events | Assessing the frequency of rare events over a specified period or area |
Interactive ENT Mindmap
Navigate through our detailed, interactive mindmap on the statistical tests you might encounterTips for Exam Preparation
To excel in statistical analysis for otolaryngology exams:- Focus on comprehensive study materials that cover a range of statistical techniques.
- Engage in active practice with exam-style questions and mock tests.
- Utilize online resources like Otoprep.com for interactive learning experiences.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Common mistakes include:- Misinterpreting data types and their appropriate statistical tests.
- Overlooking the importance of data distribution in selecting the right analysis method.
- Ignoring the nuances of different data structures.
- Regularly reviewing and testing your understanding of key concepts.
- Seeking clarification on complex topics from mentors or through reliable online platforms.
Conclusion
In summary, mastering statistical analysis is essential for success in otolaryngology board exams. The knowledge of these concepts not only aids in exam preparation but also enhances clinical decision-making skills. Remember, consistent practice and a thorough understanding of statistical principles are key to excelling in these examinations.Unveil the Secrets of Inner Ear Anatomy & Embryology - Ace Your ENT Exams with OtoPrep


Unlock Expert Insights into Inner Ear Anatomy and Embryology
Introduction
Embark on a detailed exploration of inner ear anatomy and embryology with OtoVoce. Our focused discussions and mindmaps are meticulously crafted to elevate your preparation for rigorous ENT examinations like ABOto, AOBOO, ABOHNS, and FRCSORLHNS, enriching your understanding and application of intricate concepts.Optimize Your ENT Examination Prep
From detailed viva discussions on embryologic malformations to meticulous examinations of cochlear structures, OtoVoce offers unparalleled insights that are indispensable for ENT MCQs, Viva Examinations, and otolaryngology examination prep. Engage with our content and ensure a robust preparation for examinations like EBEORLHNS and FRCSENT.Expert-led Video Discussion
Interactive ENT Mindmap
Navigate through our detailed, interactive mindmap, a visual treat that simplifies complex concepts in ear anatomy and embryology.Engage & Explore More with OtoVoce
Connect with OtoVoce and immerse yourself in a reservoir of knowledge, ideal for acing ENT Viva examinations and mastering ENT mindmaps. Follow us on our social channels and dive deeper into the enthralling world of otolaryngology with experts.All You Need To Know About Taking The FRCS ORL HNS Section 1 and Section 2 examinations

All You Need To Know About Taking The FRCS ORL HNS Section 1 and Section 2 examinations
Preparing for the FRCS ORL HNS examinations? Here is an all-inclusive guide to help you navigate through this challenging yet rewarding journey. We aim to provide detailed insights into the registration process, eligibility, exam formats, and preparation strategies, ensuring you’re fully prepared to ace these prestigious exams.Understanding the FRCS ORL HNS Examinations
The FRCS ORL HNS examinations are rigorous and designed to evaluate the proficiency of doctors specializing in Otolaryngology in the United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland. The exams are divided into two parts: Section 1 (written exam) and Section 2 (clinical and oral exam). Successful completion of these exams demonstrates a high level of competence in the field and opens up new avenues in the medical profession.Eligibility Criteria for the FRCS ORL HNS Examinations
The FRCS ORL HNS examinations, designed by the Joint Committee on Intercollegiate Examinations (JCIE), serve as a crucial step in demonstrating proficiency and achieving certification in Otolaryngology. The following prerequisites are mandatory for applicants considering sitting for these examinations:
- Medical Qualification: Applicants must hold a medical qualification recognized for registration by either the General Medical Council of the United Kingdom or the Medical Council of Ireland. Additionally, they must have been qualified for at least six years.
- Standard of Clinical Competence: Applicants need to show evidence of reaching the standard of clinical competence as defined in the Intercollegiate Surgical Curriculum. This standard is usually met for the award of the Certificate of Completion of Training (CCT) by the General Medical Council or for the award of Certificate of Completion of Specialist Training (CCST) by the Irish Surgical Postgraduate Training Committee. The required standard could be achieved through training, qualifications, and experience considered collectively. Please note that passing the Intercollegiate Specialty Examination alone does not guarantee automatic attainment of the CCT, CCST (Ireland), or placement on the Specialist Register; the Examination only forms part of the evidence required.
- References: Applicants are required to provide three structured references in the format prescribed by the JCIE. These references must be completed by appropriate senior colleagues who have direct experience of the applicant’s current clinical practice in the relevant specialty. More information can be found in the Guidance Notes for Referees.
- Examination Attempt Limits: The JCIE stipulates a maximum limit on examination attempts. Candidates are granted up to a seven-year period to complete the examination process, which is divided into two sections:
- Section 1: Candidates have a two-year period from their first attempt with a maximum of four attempts and no re-entry.
- Section 2: After achieving the required standard in Section 1 and gaining eligibility to proceed to Section 2, candidates are allowed a maximum of four attempts with no re-entry.
It is essential to consider these prerequisites before applying for the FRCS ORL HNS examinations. Meeting these standards reflects a high level of competence and readiness to excel in these examinations and a career in otolaryngology.
How to Register for the FRCS ORL HNS Section 1 and Section 2 Examination
Candidates looking to undertake the FRCS ORL HNS examination need to register through the official JCIE website. The registration process is straightforward and easy to navigate. To start your registration, visit the JCIE website at this link. The registration fee for Section 1 examination is £630. The examination is typically held twice a year, in January and July, at various locations throughout the United Kingdom. Upon successful completion of Section 1, candidates can then proceed to register for Section 2 on the same JCIE website. The registration fee for Section 2 is £1230. Similar to Section 1, Section 2 is also conducted twice annually, usually around November and April. Remember to stay updated with the exam dates and venues as they are subject to change. Candidates are also encouraged to review all relevant materials and regulations on the JCIE website before registering.Section 1: Written Examination
Section 1 is a computer-based written test delivered via Pearson VUE Test Centres in the UK and Ireland. It’s composed of two Single Best Answer (SBA) papers, each containing 120 questions to be completed in 2 hours and 15 minutes. These papers cover the curriculum content that can be best assessed in a written format. Candidates must meet the required standard in Section 1 to proceed to Section 2.Preparing for Section 1
Given the breadth of topics covered, it’s crucial to have a systematic approach to your revision. A good place to start is the Intercollegiate Surgical Curriculum Programme (ISCP) which provides the foundation for the FRCS ORL HNS examinations. Reviewing past papers and using question banks like OtoPrep can also be extremely beneficial in your preparations.JCIE Sample Question for Section 1:
Question 1: This 67 year old man previously underwent a total laryngectomy and bilateral selective neck dissections for a T4 supraglottic carcinoma. Two months following completion of his adjuvant radiotherapy he presents with a discharging wound in his neck. Dye swallow confirms the presence of a pharyngocutaneous fistula. What would be the next most appropriate step in his management?Question 2: A 42 year old woman presents with a 4 mm lesion on her forehead. A punch biopsy shows this is a superficial basal cell carcinoma with a depth of invasion of 0.3mm. From the options shown below, choose the single most appropriate teatment after considering cosmesis and cure rates.
Question 3: A 65 year old man who had an implantable cardioconverter-defrillator (ICD) fitted previously, underwent a laryngopharyngo-oesphagectomy, but unfortunately his condition deteriorated and he became comatose. The medical consensus is that he should have his ICD switched off. The patient has not provided an advance directive and his relatives cannot come to a united decision. Which of the following is the next most appropriate course of action?
OtoPrep Sample Questions:
Question 1: A 60-year-old woman with a history of chronic sinusitis presents to the otolaryngology clinic with sudden onset of left-sided facial pain, headache, and unilateral vision loss. Imaging reveals inflammation within the sphenoid sinus and an occlusion of the left internal carotid artery, with the involvement of the posterior communicating artery suspected. Which part of the carotid siphon does the posterior communicating artery arise from?- A. Horizontal segment
- B. Ascending segment
- C. First genu
- D. Descending segment
- E. Second genu
Explanation The second genu of the carotid siphon, a portion of the cerebral segment of the internal carotid artery, gives off the posterior communicating artery. The carotid siphon is a term used to describe the S-shaped portion of the internal carotid artery in the cavernous sinus. It is divided into four parts: the horizontal segment, the ascending segment, the first genu, and the descending segment, which then turns to become the second genu. A potentially usedful mnemonic to remember the order of the carotid siphon segments is “HAFD” (Horizontal, Ascending, First genu, Descending)
Question 2: A 35-year-old female patient presents to the otolaryngology clinic with a history of progressive hearing loss in both ears over the past two years. She reports occasional tinnitus and difficulty understanding speech, particularly in noisy environments. There is no history of otalgia, otorrhea, or vertigo. On otoscopic examination, both tympanic membranes appear normal, and no masses or lesions are observed in the external auditory canals. Audiometric testing reveals bilateral conductive or mixed hearing loss. The audiologist considers using masking during the test to ensure accurate results.
In the context of this patient’s audiometric testing, what is the “masking dilemma”?
Answer: D. The phenomenon where masking one ear can inadvertently raise the threshold of the non-masked ear
Explanation: The “masking dilemma” refers to a phenomenon that can occur during audiometric testing when masking noise is introduced to one ear to prevent crossover of sound. In cases of bilateral conductive or mixed hearing loss, the masking noise may inadvertently raise the hearing threshold of the non-masked ear, making it difficult to accurately assess the true hearing thresholds. This dilemma can complicate the interpretation of audiometric results and may necessitate additional testing or the use of alternative masking techniques to accurately assess the patient’s hearing loss.
Section 2: Clinical and Oral Examination
Section 2 is the clinical component of the examination, consisting of a series of carefully designed and structured interviews on clinical topics. Some are scenario-based, while others revolve around volunteers who are past or present patients relevant to the specialty. Section 2 examinations take place in pre-selected UK/Ireland host centres.Examination format:
Section 2 consists of the following components:- History Taking & Communication Skills (1 x 20-minute session) with actors present
- Clinical short cases on the following domains: (2 x 20-minute sessions)
- Otology including Neuro‐Otology and Head & Neck Surgery
- Paediatric Otolaryngology and Rhinology & Facial Plastics
- 4 x 30-minute oral examinations on the following topics:
- Otology including Neuro‐Otology
- Head & Neck Surgery
- Paediatric Otolaryngology
- Rhinology & Facial Plastics
Preparing for Section 2
For Section 2, real-life clinical exposure, practice, and revision are crucial. Participating in otolaryngology clinics and theatre sessions will help familiarize you with common cases and presentations. It is also recommended to join study groups, where you can learn from your peers and practice mock viva questions.JCIE Sample Questions for Section 2:
Question: OtologyTheme: Otosclerosis
Scenario: A 45 year old woman has been diagnosed with unilateral otosclerosis. She has tried a hearing aid and wishes to proceed with surgery.
Introductory question: Based an integration of information presented/application of basic principles to the situation described in the scenario/differential diagnosis e.g. What are the risks of stapes surgery?
Points for discussion: Persistent conductive loss, sensorineural loss? Incidence Loss of taste VIIn damage, Vertigo? Cause, post op serous labyrinthitis, BPPV, Delayed fistula, gush
Question 2: Based on management, relevant applied pathophysiology, anatomy e.g. When wouldn’t you operate on this patient?
Points for discussion: Only hearing ear – what is the other ear like Audiological criteria A-B gap closed within 10db of better ear Occupation, leisure activities Menieres disease/Hydrops due to distension of saccule Anaesthetic risk factors
Question 3: Based on complications of management e.g. During the procedure you have caused a floating footplate. How would you manage this complication?
Points for discussion: Cover with graft and abandon the procedure, apply vein graft and place prosthesis on footplate Drill an inferior marginal slot and remove the footplate then proceed with vein graft and large diameter prosthesis
Final Words
The FRCS ORL HNS exams are a significant step in your medical career. They require diligent preparation and a deep understanding of otolaryngology. With the right resources and strategies, you can confidently approach these exams. Remember, consistent study, exposure to a variety of clinical cases, and regular practice of examination questions are the keys to success. Good luck with your preparations!References
- Royal College of Surgeons of England. FRCS (ORL-HNS) Examination
- British Association of Otorhinolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery. The intercollegiate examination in ORL-HNS
- Bradley, P. J., Simo, R., Reddy-Kolanu, G., Kerawala, C. J., & Lloyd, S. (2017). The new section 1 examination for the Fellowship of the Royal College of Surgeons in Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (FRCS ORL-HNS): some early reflections. The Journal of Laryngology & Otology, 131(3), 187-189.
- Ahmed, J., & Jefferis, A. (2018). The Intercollegiate Examination in Otolaryngology: Tips for Successful Preparation. The Otorhinolaryngologist, 11(1), 31-35.
- Gurney, T. (2019). Preparing for the FRCS ORL-HNS Examinations: A Personal Perspective. Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England, 101(6), 462-465.
Quick Links
Functional Always active
Preferences
Statistics
Marketing
We noticed you're visiting from United Kingdom (UK). We've updated our prices to Pound sterling for your shopping convenience. Use United States (US) dollar instead. Dismiss
